"Mastering Polymorphism in Java: A Technical Deep Dive 🚀💻"
Discover the Enchanted World Where Java Code Comes to Life! 🌟👾🚀
Table of contents
- #CodeMagicLaughs🚀
- Introduction:
- What is Polymorphism?
- Meet the Two Dynamic Duos: Compile-time and Runtime Polymorphism
- Compile-time Polymorphism (Static Binding)
- Runtime Polymorphism (Dynamic Binding)
- 1. Compile-time Polymorphism (Static Binding)
- 2. Runtime Polymorphism (Dynamic Binding)
- Why Should You Care?
- Because Polymorphism is the Coolest Party Trick!
- Advantages of Polymorphism in Java
- Disadvantages of Polymorphism in Java
- Conclusion: OOP Series Finale! 🚀
- 🚀 Recap:
- 🌌 Next Series:
- #CodeMagicLaughs
- Happy coding! 🚀
#CodeMagicLaughs🚀
Introduction:
Greetings, fellow coding superheroes! Today, we're donning our capes and diving into the epic saga of polymorphism—a superpower in the dynamic universe of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). Buckle up, because we're about to embark on a heroic quest where objects transform like superheroes and code becomes a thrilling adventure!
What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism, derived from the Greek words "poly" (many) and "morphos" (forms), refers to the ability of a single entity to take various forms. In the context of OOP, this translates into a programming paradigm that allows objects of different types to be treated as objects of a common type.
Meet the Two Dynamic Duos: Compile-time and Runtime Polymorphism
Compile-time Polymorphism (Static Binding)
Runtime Polymorphism (Dynamic Binding)
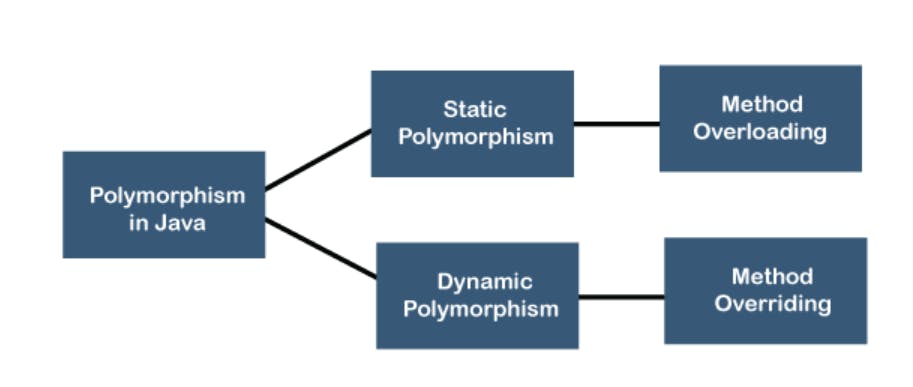
1. Compile-time Polymorphism (Static Binding)
Compile-time polymorphism, also known as static binding or method overloading, occurs when multiple methods in the same class have the same name but different parameters. The compiler determines which method to invoke based on the method signature.
class Calculator {
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}
2. Runtime Polymorphism (Dynamic Binding)
Runtime polymorphism, or dynamic binding, is achieved through method overriding. It allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass. The decision of which method to execute is made during runtime.
class Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Some generic sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bark");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow");
}
}
Why Should You Care?
Because Polymorphism is the Coolest Party Trick!
Code Reusability: Polymorphism promotes the reuse of code through the implementation of interfaces and abstract classes, fostering modular and maintainable codebases.
Flexibility: By allowing objects to take different forms, polymorphism enables developers to write more generic and adaptable code.
Enhanced Readability: Polymorphic code tends to be more readable and comprehensible, as it reflects the real-world relationships between objects.
Advantages of Polymorphism in Java
Increases code reusability by allowing objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common class.
Improves readability and maintainability of code by reducing the amount of code that needs to be written and maintained.
Supports dynamic binding, enabling the correct method to be called at runtime, based on the actual class of the object.
Enables objects to be treated as a single type, making it easier to write generic code that can handle objects of different types.
Disadvantages of Polymorphism in Java
This can make it more difficult to understand the behavior of an object, especially if the code is complex.
This may lead to performance issues, as polymorphic behavior may require additional computations at runtime.
Conclusion: OOP Series Finale! 🚀
As we wrap up our OOP superhero series—Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstraction—we've unraveled the Java coding magic. Get ready for the next thrill! 🌟
🚀 Recap:
Encapsulation: Data security fortresses.
Inheritance: Traits passed through generations.
Polymorphism: Objects dancing in flexibility.
Abstraction: Magic simplifying complexities.
🌌 Next Series:
Constructors & Methods! Stay tuned for our next coding adventure with constructors and methods, promising fresh creativity bursts. Thanks for being part of the OOP saga. More excitement awaits! 🦸♂️💡🚀 #Java #OOPAdventure #ConstructorsUnleashed

