"Java Interface Essentials: Elevating Code Design and Collaboration"
Discover the Enchanted World Where Java Code Comes to Life! 🌟👾🚀
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction:
- 2. What's the Buzz about Interfaces?
- 3. What are Interfaces in Java?
- 4. Syntax for Java Interfaces
- 5. Uses of Interfaces in Java
- 6. Relationship Between Class and Interface
- 7. Difference Between Class and Interface
- 8. Why Interfaces?
- 9. How to declare an interface?
- 10. Multiple inheritances in Java by interface
- Conclusion: Interface Mastery Unleashed!
- Happy coding! 🚀
1. Introduction:
Greetings, fellow code enthusiasts! Today, we're delving into a concept that's more than just a set of rules; it's a game-changer in the Java programming arena. Buckle up as we explore the magical realm of interfaces!
#CodeMagicLaughs🦸♂️
2. What's the Buzz about Interfaces?
Interfaces in Java are like the superhero capes of the coding world. They define a set of rules without getting into the nitty-gritty details of how those rules are implemented. Think of them as contracts that classes sign, promising to deliver specific functionalities.
3. What are Interfaces in Java?
The interface in Java is a mechanism to achieve abstraction.
There can be only abstract methods in the Java interface, not the method body.
It is used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritances in Java using Interface.
In other words, you can say that interfaces can have abstract methods and variables. It cannot have a method body. Java Interface also represents the IS-A relationship.
It cannot be instantiated just like the abstract class.
Since Java 8, we can have default and static methods in an interface.
Since Java 9, we can have private methods in an interface.

4. Syntax for Java Interfaces
public interface MyInterface {
// Constant declarations (optional)
type CONSTANT_NAME = value;
// Abstract method declarations
returnType methodName(parameterList);
// More abstract method declarations
// Default method (Java 8 and later)
default returnType methodName() {
// Method implementation
}
// Static method (Java 8 and later)
static returnType methodName() {
// Method implementation
}
}
Explanation:
public interface MyInterface: Declares a public interface namedMyInterface.
type CONSTANT_NAME = value;: Defines constants (optional).
returnType methodName(parameterList);: Declares abstract methods.
default returnType methodName() { ... }: Provides a default implementation for a method (Java 8 and later).
static returnType methodName() { ... }: Defines a static method within the interface (Java 8 and later).
5. Uses of Interfaces in Java
Uses of Interfaces in Java are mentioned below:
It is used to achieve total abstraction.
Since java does not support multiple inheritances in the case of class, by using an interface it can achieve multiple inheritances.
Any class can extend only 1 class but can any class implement an infinite number of interface.
It is also used to achieve loose coupling.
Interfaces are used to implement abstraction.
Some questions arise here, those are
- why use interfaces when we have abstract classes?
Answer:- The reason is, abstract classes may contain non-final variables, whereas variables in the interface are final, public, and static.
// A simple interface interface Player { final int id = 10; int move(); }
6. Relationship Between Class and Interface
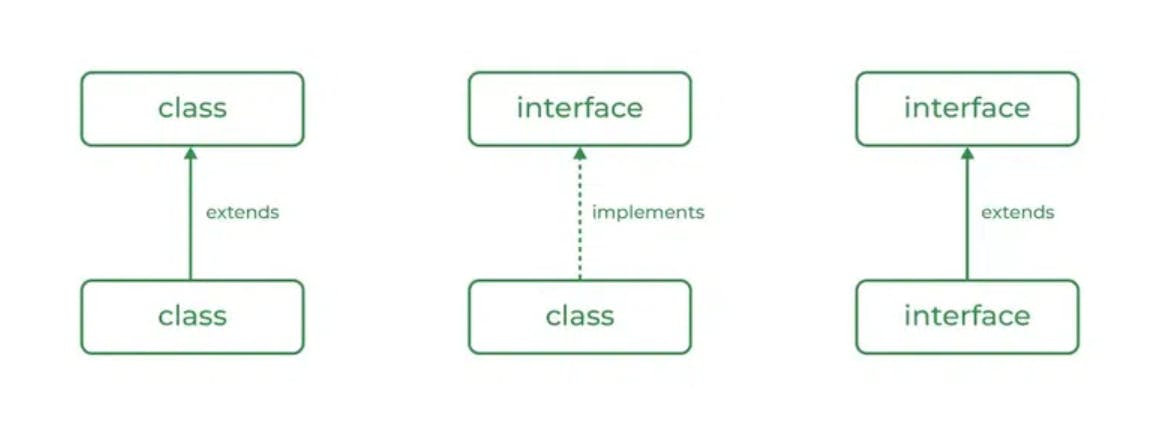
A class can extend another class similar to this, and an interface can extend another interface. But only a class can extend to another interface, and vice-versa is not allowed.
7. Difference Between Class and Interface
The major differences between a class and an interface are mentioned below:
| Class | Interface |
| In class, you can instantiate variables and create an object. | In an interface, you can’t instantiate variables and create an object. |
| A class can contain concrete(with implementation) methods | The interface cannot contain concrete(with implementation) methods |
| The access specifiers used with classes are private, protected, and public. | In Interface only one specifier is used- Public. |
8. Why Interfaces?

9. How to declare an interface?
An interface is declared by using the interface keyword.
It provides total abstraction; which means all the methods in an interface are declared with the empty body, and all the fields are public, static, and final by default.
A class implementing an interface must implement all the methods declared in the interface.
interface <interface_name>{
// declare constant fields
// declare methods that abstract
// by default.
}//End Interface
10. Multiple inheritances in Java by interface
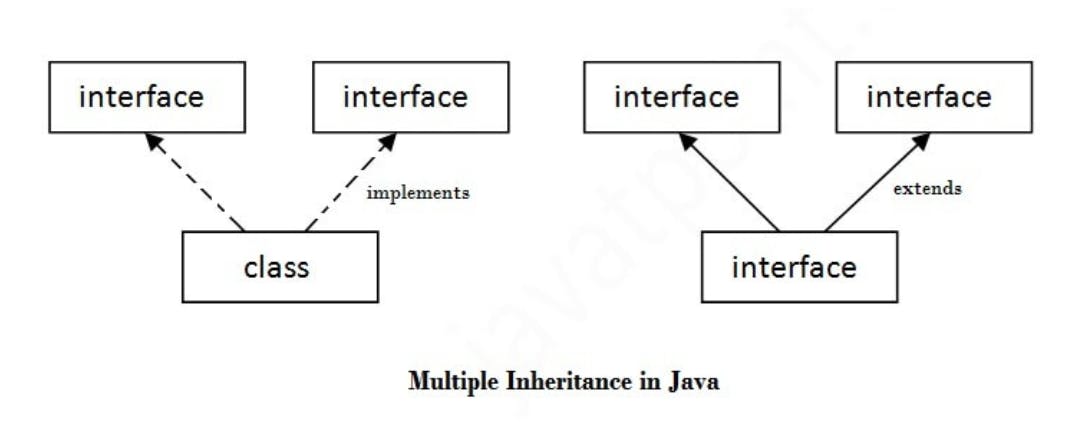
If a class implements multiple interfaces, or an interface extends multiple interfaces, it is known as multiple inheritance.
Conclusion: Interface Mastery Unleashed!
In the wild world of Java, interfaces are more than rules—they're the secret sauce to coding magic! 🎩✨ As we wrap up this journey, brace for impact! The Java adventure continues with even more magic and surprises. Get ready to rock the code! 🚀 #JavaInterfacesMagic
Keep coding, keep exploring, and stay tuned for the next chapter Static Keyword in the Java saga! 🚀✨

